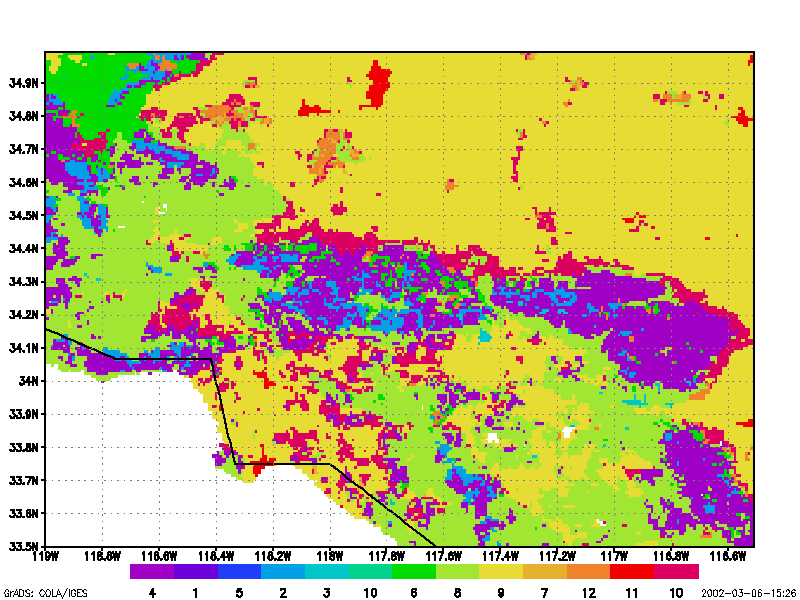
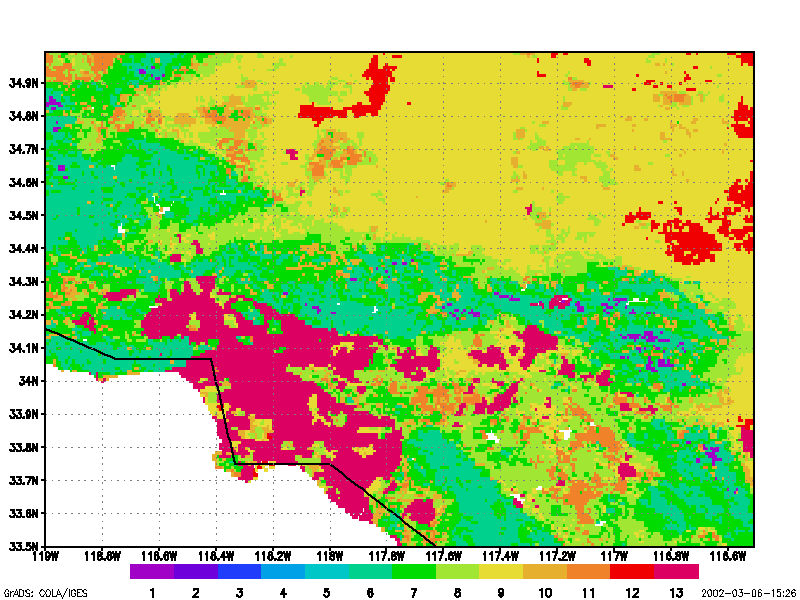
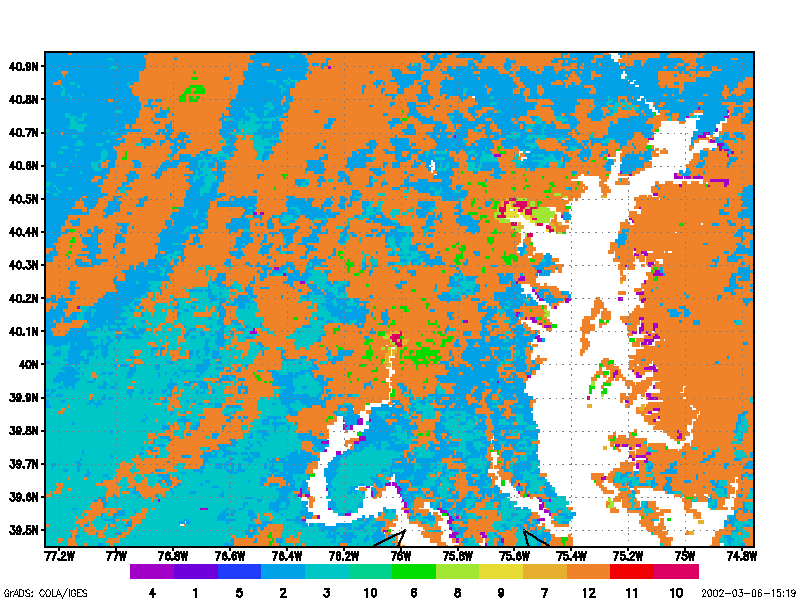
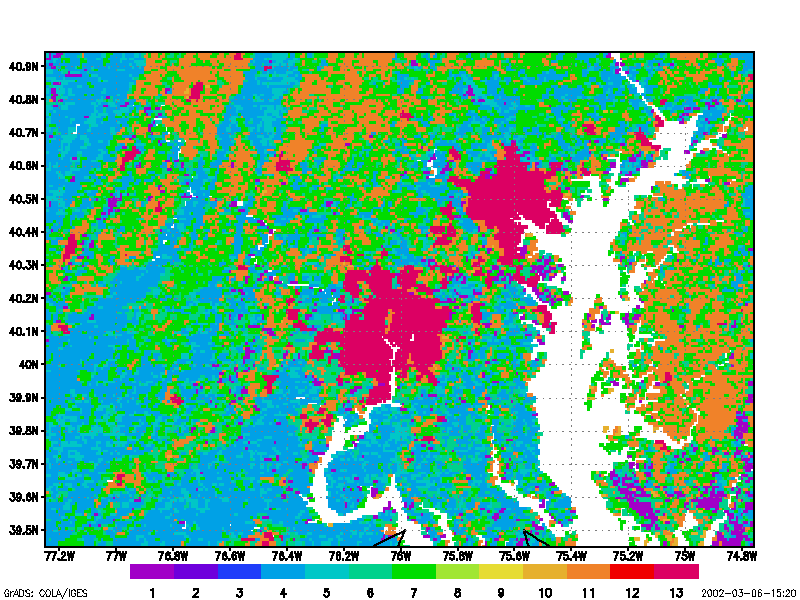
Digital images of the Earth obtained by satellites and aircraft represent one of the fastest growing applications in environmental science. This course builds upon concepts first introduced in Geography 169 (“Introduction to Remote Sensing and Imaging GIS”), but provides a more complete treatment of the digital processing methods required for manipulating and analyzing image data. Topics covered include statistical description, geometric correction and removal of terrain distortion, radiometric corrections for illumination and atmospheric effects, classification routines, image enhancement and filtering, image display, and change detection schemes. Most of these algorithms are presented using simple algebra. Procedures presented in lecture are reinforced with a series of laboratory exercises and a student project.
In statistical description, basic concepts and both univariate and multivariate statistical methods are presented. Discussion of radiometric and geometric corrections includes relative image normalization and absolute radiometric techniques to correct atmospheric attenuation. Rectification procedures include image-to-map rectification and image-to-image registration.
Methods for image enhancement include linear and non-linear approaches of image histogram manipulation. Spatial and directional filters, such as edge-preserving median, adaptive band-pass, embossing filter and Fourier transforms, are presented. Vegetation indices are also discussed.
Both supervised and unsupervised methods for image classification are presented. Treatment of supervised classification includes concepts of signature extension and problems of geographical stratification that often arise during image classification. All commonly used classification algorithms are described. Because detection of environmental change is one of the fastest-growing applications in remote sensing, different methods for detecting changes on the Earth surface are discussed. Finally, scale issues in remote sensing are presented.
Grading:
1/3 Lab
1/3 First hourly exam
1/3 Second hourly exam
Textbook:
John R. Jensen, 1996: Introductory digital image processing (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall, 316pp.
Reader (for lab)
Reference:
Lillesand and Kiefer, 1994: Remote sensing and image interpretation (3rd ed.) John Wiley & Sons, 749pp.
Provisional Schedule:
Week 1 (1) Introduction to digital image processing of remote sensed data and image processing system consideration (2) Initial statistic extraction
Week 2 Geometric correction of remote sensor data Lab 1. Image display and statistics.
Week 3 Radiometric correction of remote sensed data Lab 2. Rectification
Week 4 Image enhancement (I) Image reduction and magnificent, contrast enhancement, spatial convolution filtering Lab 3. Imagery on the Internet
Week 5 Image enhancement (II) Fourier transform, special transformations Lab 4. Image data processing (I) Contrast stretching and quick filtering, Convolution filter
Week 6 Image classification (I) Supervised classification Mid-term
Week 7 Image classification (II) unsupervised classification Lab 5. Image data processing (II) Principal Component Analysis and fast Fourier Transfer
Week 8 Digital change detection Lab 6. Vegetation classification (supervised and unsupervised)
Week 9 Scale in remote sensing (I) Lab 7. Vegetation classification (post-classification)
Week 10 Scale in remote sensing (II); The NASA remote sensing project Lab 8 continue